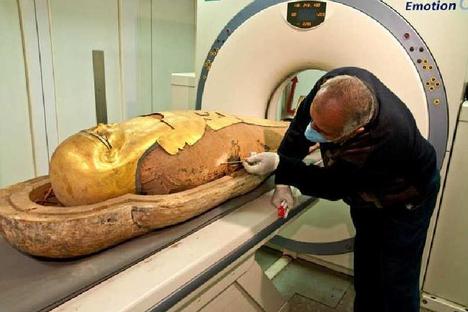
 “Scientists scanned 20 mummies, and examined scans of two more, for the study.” Source of caption and photo: online version of the WSJ article quoted and cited below.
“Scientists scanned 20 mummies, and examined scans of two more, for the study.” Source of caption and photo: online version of the WSJ article quoted and cited below.
(p. A5) ORLANDO, Fla. — Researchers said they found evidence of hardening of the arteries in Egyptian mummies dating as far back as 3,500 years, challenging longstanding assumptions that cardiovascular disease is mainly a malady of modern societies.
A team of heart-imaging experts and Egyptologists examined 22 mummies from the Egyptian National Museum of Antiquities in Cairo in a CT scanning machine, looking for evidence of calcium buildup that could indicate vascular disease.
They were able to identify the hearts, arteries or both in 16 of the mummies, nine of whom had deposits of calcification. An analysis determined the deposits were either definite or probable evidence of atherosclerosis, the condition that leads to heart attacks and strokes.
“Not only do we have atherosclerosis now, it was prevalent as long as 3,500 years ago,” said Gregory Thomas, a cardiologist and imaging specialist at University of California, Irvine, who was principal investigator of the study. “It is part of the human condition.”
The research was presented Tuesday at the American Heart Association scientific meeting here. A report is also scheduled to appear in Wednesday’s issue of the Journal of the American Medical Association.
For the full story, see:
RON WINSLOW. “Heart Disease Found in Egyptian Mummies.” The Wall Street Journal (Weds., NOVEMBER 18, 2009): A5.
(Note: the online version of the article has a date of NOVEMBER 19, 2009 and is titled “Heart Disease Found in Egyptian Mummies.”)
