 "LOVE PREVAILS. A bride and groom, surrounded by friends and a band, dressed for their wedding photos last week in Baghdad." Source of caption and photo: online version of the NYT article quoted and cited below.
"LOVE PREVAILS. A bride and groom, surrounded by friends and a band, dressed for their wedding photos last week in Baghdad." Source of caption and photo: online version of the NYT article quoted and cited below.
(p. A1) BAGHDAD, Nov. 19 — Five months ago, Suhaila al-Aasan lived in an oxygen tank factory with her husband and two sons, convinced that they would never go back to their apartment in Dora, a middle-class neighborhood in southern Baghdad.
Today she is home again, cooking by a sunlit window, sleeping beneath her favorite wedding picture. And yet, she and her family are remarkably alone. The half-dozen other apartments in her building echo with emptiness and, on most days, Iraqi soldiers are the only neighbors she sees.
“I feel happy,” she said, standing in her bedroom, between a flowered bedspread and a bullet hole in the wall. “But my happiness is not complete. We need more people to come back. We need more people to feel safe.”
Mrs. Aasan, 45, a Shiite librarian with an easy laugh, is living at the far end of Baghdad’s tentative recovery. She is one of many Iraqis who in recent weeks have begun to test where they can go and what they can do when fear no longer controls their every move.
The security improvements in most neighborhoods are real. Days now pass without a car bomb, after a high of 44 in the city in February. The number of bodies appearing on Baghdad’s streets has plummeted to about 5 a day, from as many as 35 eight months ago, and suicide bombings across Iraq fell to 16 in October, half the number of last summer and down sharply from a recent peak of 59 in March, the American military says.
As a result, for the first time in nearly two years, people are moving with freedom around much of this city. In more than 50 interviews across Baghdad, it became clear that while there were still no-go zones, more Iraqis now drive between Sunni and Shiite areas for work, shopping or school, a few even after dark. In the most stable neighborhoods of Baghdad, some secular women are also dressing as they wish. Wedding bands are playing in public again, and at a handful of once shuttered liquor stores customers now line up outside in a collective rebuke to religious vigilantes from the Shiite Mahdi Army.
Iraqis are clearly surprised and relieved to see (p. A8) commerce and movement finally increase, five months after an extra 30,000 American troops arrived in the country.
For the full story, see:
(Note: the slightly different online title was "Baghdad’s Weary Start to Exhale as Security Improves.")
 "COMMERCE RETURNS. A Baghdad market, shut by violence, recently reopened." Source of caption and photo: online version of the NYT article quoted and cited above.
"COMMERCE RETURNS. A Baghdad market, shut by violence, recently reopened." Source of caption and photo: online version of the NYT article quoted and cited above.



 Source of the map: online version of the NYT article cited above.
Source of the map: online version of the NYT article cited above. 




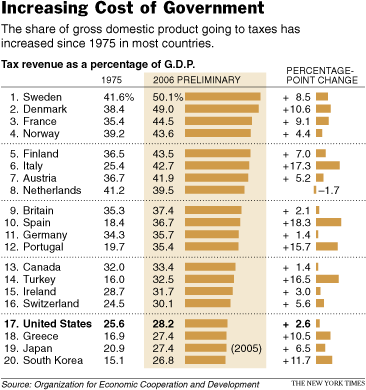 Source of graph: online version of the NYT article quoted and cited below.
Source of graph: online version of the NYT article quoted and cited below.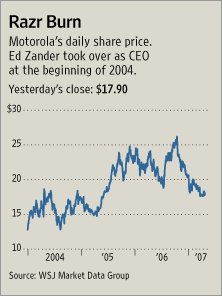 Source of graph: online version of the WSJ article cited below.
Source of graph: online version of the WSJ article cited below. Motorola CEO. Source of image: online version of the WSJ article cited above.
Motorola CEO. Source of image: online version of the WSJ article cited above.
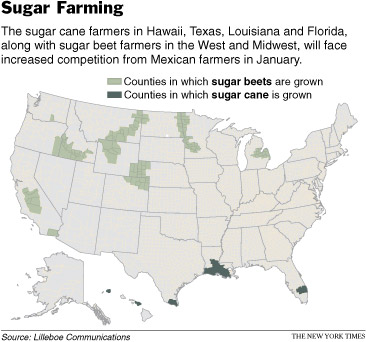 Source of graphic: online version of NYT article cited above.
Source of graphic: online version of NYT article cited above.