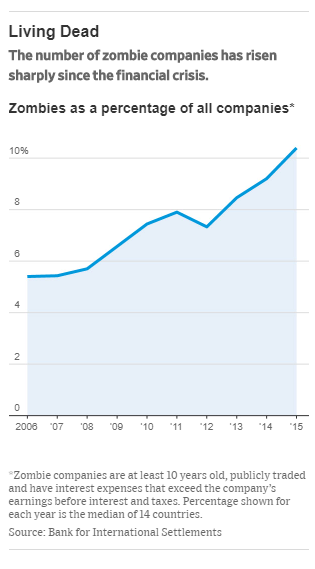
Source of graph: online version of the WSJ article quoted and cited below.
(p. A1) Italian clothing maker and retailer Stefanel SpA became famous for its knitted coats and cardigans.
Many economists, investors and bankers know Stefanel as something starkly different: a zombie company. It has posted an annual loss for nine of the last 10 years and restructured its bank debt at least six times, including several grace periods when Stefanel only had to pay interest on what it owed.
After booming during Italy’s post-World War II expansion, Stefanel and its lumbering factories were overwhelmed by Spanish fast-fashion giant Zara and then battered by the economic slowdown that hit Italy in 2008.
Stefanel is still alive but staggering. So are hundreds of other chronically unprofitable, highly indebted companies being kept afloat with new infusions from lenders and shareholders, especially in Southern Europe.
Economists and central bankers say zombies undercut prices charged by healthier competitors, create artificial barriers to entry and prevent the flushing out of (p. A10) weak companies and bad loans that typically happens after downturns.
Now that the European economy is in growth mode, those zombies and their related debt problems could become a drag on the entire continent.
“The zombification of the corporate sector and banks [is] a risk for future living standards,” Klaas Knot, a European Central Bank governor and the head of the Dutch central bank, said in an interview.
. . .
In some ways, zombie firms are an unintended side effect of years of easy money from the ECB, which rolled out aggressive stimulus policies, including negative interest rates, to support lending and growth. Those policies have been sharply criticized in some richer eurozone countries for making it easier for banks to keep struggling corporate borrowers alive.
For the full story, see:
Eric Sylvers and Tom Fairless. “Zombie Companies Haunt Europe’s Economic Recovery.” The Wall Street Journal (Thursday, November 16, 2017): A1 & A10.
(Note: ellipsis added.)
(Note: the online version of the article has the date Nov. 15, 2017, and the title “A Specter Is Haunting Europe’s Recovery: Zombie Companies.”)

