 “At the Dahon bicycle plant in Shenzhen, China, pay has risen 10 to 15 percent a year, but productivity gains have held down costs.” Source of caption and photo: online version of the NYT article quoted and cited below.
“At the Dahon bicycle plant in Shenzhen, China, pay has risen 10 to 15 percent a year, but productivity gains have held down costs.” Source of caption and photo: online version of the NYT article quoted and cited below.
(p. A1) SHENZHEN, China, Aug. 28 — At the Dahon bicycle factory here, Zhang Jingming’s fingers move quickly and methodically — grabbing bicycle seats, wrapping them in cardboard and smoothly attaching them to frames.
Working a 45-hour week, Mr. Zhang makes the equivalent of $263 a month; as recently as February, he was making just $197. Some of his higher pay comes from working more efficiently. “When I first started, I wasn’t this fast,” he said.
But a good portion reflects a raise Mr. Zhang got: to 1.45 cents for each bicycle seat from 1.32 cents. It is a small difference that signifies major change.
Chinese wages are on the rise. No reliable figures for average wages exist; the government’s economic data are notably unreliable. But factory owners and experts who monitor the nation’s labor market say that businesses are having a hard time finding able-bodied workers and are having to pay the workers they can find more money.
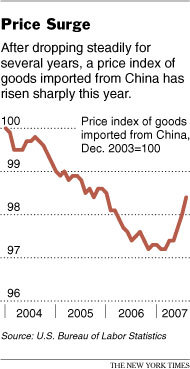
And higher wages in China are likely to lead to higher prices in the United States — at the mall, at the grocery, even at the gas pump.
Chinese companies are already passing along some of their higher costs to overseas customers. Prices for goods from China, after years of gradual decline, have risen 1.2 percent since February, according to the Labor Department. July’s increase was the biggest yet: 0.4 percent compared with June. Chinese companies and contractors are also passing on the cost of the rising value of their currency, the yuan, up 8.8 percent against the dollar in the last two years.
For decades, many labor economists said that China’s vast population would supply a nearly bottomless pool of workers. So many people would be seeking jobs at any given time, this rea-(p. A9)soning went, that wages in this country would be stuck just above subsistence levels. As recently as four years ago, some experts estimated that most of the perhaps 150 million underemployed workers in the countryside would be heading to cities.
Instead, sporadic labor shortages started to appear in 2003 at factories in the Pearl River delta of southeastern China. Now those shortages have spread to factories up and down the Chinese coast, specialists say.
. . .
(p. A9) The hardest variable to judge in China’s changing labor market is the pace of productivity growth. Since there are few reliable statistics, the best way to assess productivity is to look at individual factories like the Dahon operation here, which produces bicycles that collapse for easy storage.
David T. Hon, chief executive of the privately held Dahon Group, said that while he had been raising wages 10 to 15 percent a year, the average labor cost for each bicycle had actually edged downward. This is possible, he said, because sales are growing 30 percent a year and increasingly large-scale production has brought savings. The cost of engineering a new bicycle design, or handling the accounting and other back-office operations, is spread over more and more bicycles as production rises.
For the full story, see:
KEITH BRADSHER. “Wages Are on the Rise in China As Young Workers Grow Scarce.” The New York Times (Weds., August 29, 2007): A1 & A9.
(Note: ellipsis added.)
 Source of graph: online version of the NYT article quoted and cited above.
Source of graph: online version of the NYT article quoted and cited above.
