I’ve slogged through enough reports from the National Academy of Sciences to know they’re often not shining examples of the scientific method. But — call me naïve — I never thought the academy was cynical enough to publish a political tract like “Beyond Bias and Barriers,” the new report on discrimination against female scientists and engineers.
. . .
I consulted half a dozen of these experts about the report, and they all dismissed it as a triumph of politics over science. It’s classic rent-seeking by a special-interest group that stands to get more money and jobs if the recommendations are adopted.
“I am embarrassed,” said Linda Gottfredson of the University of Delaware, “that this female-dominated panel of scientists would ignore decades of scientific evidence to justify an already disproved conclusion, namely, that the sexes do not differ in career-relevant interests and abilities.”
. . .
After decades of schools pushing girls into science and universities desperately looking for gender diversity on their faculties, it’s insulting to pretend that most female students are too intimidated to know their best interests. As Science magazine reported in 2000, the social scientist Patti Hausman offered a simple explanation for why women don’t go into engineering: they don’t want to.
“Wherever you go, you will find females far less likely than males to see what is so fascinating about ohms, carburetors or quarks,” Hausman said. “Reinventing the curriculum will not make me more interested in learning how my dishwasher works.”
For the full commentary, see:
JOHN TIERNEY. "Academy of P.C. Science." The New York Times (Tues., September 26, 2006): A23.
(Note: the title of the online version was "Academy of P.C. Sciences.")
(Note: ellipses added.)


 Steve Jobs at left, and Steve Wozniak at right, in San Francisco in 1977. Source of photo: online version of the WSJ article cited above.
Steve Jobs at left, and Steve Wozniak at right, in San Francisco in 1977. Source of photo: online version of the WSJ article cited above.
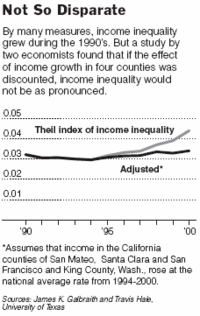
 Source of graphic: online version of the NYT article cited below.
Source of graphic: online version of the NYT article cited below.

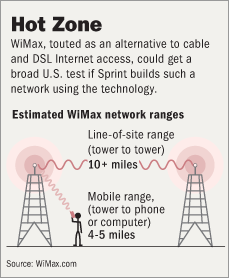 Source of graphic: online version of the WSJ article cited below.
Source of graphic: online version of the WSJ article cited below.