 Source of book image: http://www.cambridge.org/catalogue/catalogue.asp?isbn=0521846951
Source of book image: http://www.cambridge.org/catalogue/catalogue.asp?isbn=0521846951
At the AEA meetings in New Orleans I heard an excellent luncheon address on entrepreneurship by R. Glenn Hubbard, the former chair of Bush’s Council of Economic Advisers, and the current Dean of the Columbia Business School.
My ears especially perked up near the end, when he mentioned some survey research that showed that people have higher job satisfaction when they have more choice. He thought that this suggested that a society with more entrepreneurs would be one with higher job satisfaction, and suggested further, that this was a topic begging for further research.
The printed version of his talk, that he graciously sent me, does not have any full references to the survey research. But I’ve done some digging, and think that it’s highly likely that he’s referring to the extensive research of Ronald Inglehart and his colleagues.
I’m going to look into this more. In the meantime, an image of one of Inglehart’s most recent books appears above, and a relevant quote from that book appears below.
(p. 288) As we demonstrated in Chapter 6, opportunities for making autonomous choices are closely linked with human happiness. This association holds true in a systematic way that operates across cultures: in all cultural zones, societies that offer their people more room for choice produce higher levels of overall life satisfaction and happiness. A society’s level of subjective well-being is a strong indicator of the human condition, and it is systematically linked with freedom of choice.
Source:
Inglehart, Ronald, and Christian Welzel. Modernization, Cultural Change, and Democracy: The Human Development Sequence. New York: Cambridge University Press, 2005.
Reference to Hubbard luncheon address:
Hubbard, R. Glenn. "Nondestructive Creation: Entrepreneurship and Management Research in the Study of Growth." Paper presented at the Joint American Economic Association/American Finance Association Luncheon, New Orleans, Jan. 4, 2008.
 "The bolt hole was designed to hide from angry textile workers." Source of caption and photo: the BBC article quoted and cited below, and viewable at http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/england/leicestershire/4791069.stm
"The bolt hole was designed to hide from angry textile workers." Source of caption and photo: the BBC article quoted and cited below, and viewable at http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/england/leicestershire/4791069.stm 

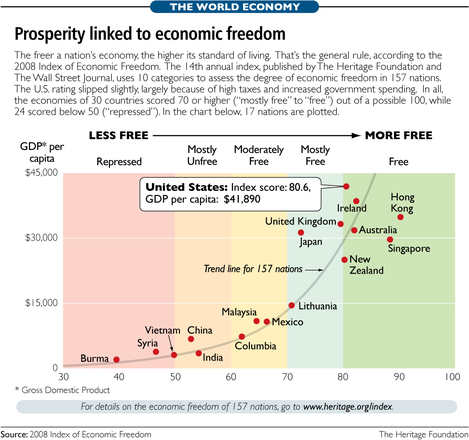
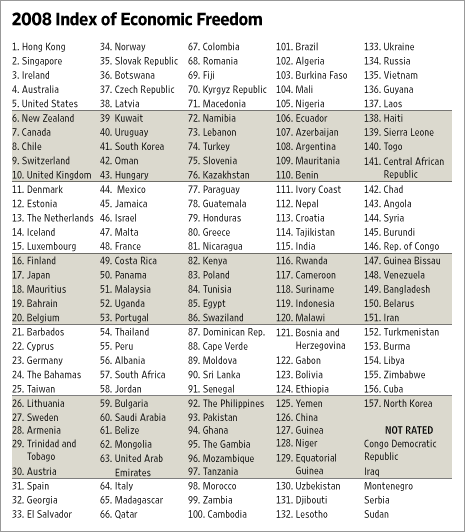 Source of table: online version of the WSJ article quoted and cited above.
Source of table: online version of the WSJ article quoted and cited above. Source of the cartoon: online version of the NYT commentary cited below.
Source of the cartoon: online version of the NYT commentary cited below. Dr. Terence Kealey is currently Vice-Chancellor at England’s only private university, the University of Buckingham. Source of photo:
Dr. Terence Kealey is currently Vice-Chancellor at England’s only private university, the University of Buckingham. Source of photo: 
 Source of book image:
Source of book image:  Lang on left; Sarkozy on right. Source of photo: online version of the NYT article quoted and cited below.
Lang on left; Sarkozy on right. Source of photo: online version of the NYT article quoted and cited below. Source of book image:
Source of book image:  "An iceberg as seen off the coast of Twillingate in Newfoundland." Source of caption and photo: online version of the WSJ article quoted and cited below.
"An iceberg as seen off the coast of Twillingate in Newfoundland." Source of caption and photo: online version of the WSJ article quoted and cited below. Brian Bryne (sic), a New York City artist, along with a partner, bought this Newfoundland house as a speculative investment. Source of photo: online version of the WSJ article quoted and cited above.
Brian Bryne (sic), a New York City artist, along with a partner, bought this Newfoundland house as a speculative investment. Source of photo: online version of the WSJ article quoted and cited above.