 Nicholas D. Kristof. Source of image: online verison of the NYT commentary cited below.
Nicholas D. Kristof. Source of image: online verison of the NYT commentary cited below.
The founding president of this country was a witch doctor who murdered tens of thousands, put enemies’ heads on pikes, denounced education and spread land mines on the road out of his country to prevent people from fleeing. This was then so vile a place that an American diplomat stabbed another to death here in 1971 and claimed in his trial that he had been driven insane partly by the screams of all the people being tortured.
When the president was finally ousted in 1979, he ran off into the bush with $60 million packed in suitcases. But he was pursued, and in a shootout, the nation’s entire foreign exchange reserves burned up.
. . .
Equatorial Guinea traditionally has been Africa’s poster boy for bad governance. Even after the old witch doctor was ousted, the kleptocracy continued under Teodoro Obiang, the current president. A new book about the country, “The Wonga Coup,” notes that in 2004 President Obiang bought a Boeing 737, one of six personal planes, for $55 million, and outfitted it with a king-sized bed and gold-plated fittings in the extra-large bathroom.
Schools and clinics are needy, but Forbes lists President Obiang as the world’s eighth richest ruler, with a net worth of $600 million. Just last year, “The Wonga Coup” says, the president’s son spent the equivalent of a third of his country’s entire education budget on a vacation home in South Africa and three cars — two Bentleys and a Lamborghini.
For the full commentary, see:
NICHOLAS D. KRISTOF. "Optimism and Africa." The New York Times (Tues., October 3, 2006): A27.
(Note: ellipsis added.)
The book mentioned in the commentary is:
Roberts, Adam. The Wonga Coup: Guns, Thugs and a Ruthless Determination to Create Mayhem in an Oil-Rich Corner of Africa. PublicAffairs, 2006.
 Source of book image: http://images.amazon.com/images/P/1586483714.01._SS500_SCLZZZZZZZ_V65100719_.jpg
Source of book image: http://images.amazon.com/images/P/1586483714.01._SS500_SCLZZZZZZZ_V65100719_.jpg


 Ful is a fava bean stew that is popular in Cairo. Source of image: online version of the NYT article cited above.
Ful is a fava bean stew that is popular in Cairo. Source of image: online version of the NYT article cited above.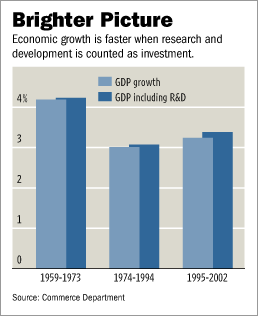 Source of graphic: online version of WSJ article cited below.
Source of graphic: online version of WSJ article cited below. Hernando de Soto and Bill Clinton at the second annual Clinton Global Initiative. Source of photo: online version of the WSJ article cited below.
Hernando de Soto and Bill Clinton at the second annual Clinton Global Initiative. Source of photo: online version of the WSJ article cited below.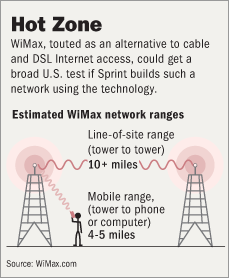 Source of graphic: online version of the WSJ article cited below.
Source of graphic: online version of the WSJ article cited below.

