Source of graphic: online version of the WSJ article quoted and cited below.
(p. B1) Big pharmaceutical companies have spent billions of dollars to buy other drug giants lately, leaving behind small biotech companies that can no longer find investors.
The biotech industry had thrived as a new-drug incubator for big pharma companies, which poured money into acquisitions and partnerships to build up their biotech-drug product line. Some of that is still happening, but most sources of investment funding have dried up in recent months.
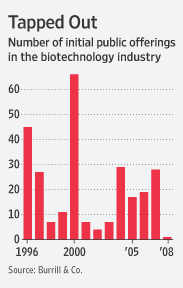
Since November, 10 biotechs have declared bankruptcy, says Ellen Dadisman, a spokeswoman for the Biotechnology Industry Organization. Meanwhile, 120 of the 360 publicly traded biotechs have less than six months of cash left, compared with just 12 companies in that position a year ago, according to Burrill & Co., a venture-capital concern in San Francisco that follows the industry.
For the full story, see:
KEITH J. WINSTEIN. “Cash Dries Up for Biotech Drug Firms.” Wall Street Journal (Mon., MARCH 16, 2009): B1.





