 Kerry Caruselle, the only passenger on her federally subsidized flight between Pueblo and Denver, leaves the plane. Source of the photo: online version of the NYT article cited below.
Kerry Caruselle, the only passenger on her federally subsidized flight between Pueblo and Denver, leaves the plane. Source of the photo: online version of the NYT article cited below. Grant Campbell has plenty of room to spread out on his federally subsidized flight between Pueblo and Denver. Source of the photo: online version of the NYT article cited below.
Grant Campbell has plenty of room to spread out on his federally subsidized flight between Pueblo and Denver. Source of the photo: online version of the NYT article cited below.
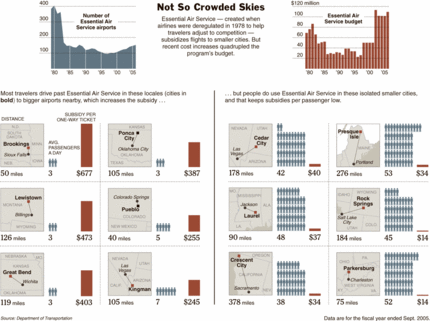
(p. A1) PUEBLO, Colo. — Hoping for an empty seat beside you on your next flight? No problem — just schedule a trip to someplace like Kingman, Ariz.; Brookings, S.D.; or Pueblo.
They are among more than 100 locales around the country that receive federally subsidized airline service, and the average number of passengers on each flight is about three.
Most of these flights on 19-seat prop planes have plenty of elbow room — a rare luxury in this age of jampacked commercial jets. Some major airlines have cut their fleets about 20 percent since 2001 and have abandoned unprofitable routes, meaning planes are flying fuller than at any time since World War II.
The more tranquil cabins come courtesy of the Essential Air Service, put in place when the airline industry was deregulated in 1978. The idea was to help travelers in smaller cities adjust to the new competitive era of air travel. The intention was for the service to go away after 10 years, but it was renewed for a second decade — and then made permanent.
Over time, though, the program has come to seem mostly expensive and, to its critics, unessential.
After all, travelers adjusted very well after deregulation, and started driving the extra distance to busier regional airports nearby that offered increasingly cheap and plentiful jet service. That left the program with (p. C7) mostly empty planes, making them more costly to fly. Add in higher maintenance and fuel costs, and spending has more than quadrupled since 1996, to $110 million.
That, of course, is not a lot in the federal scheme of things. But the program is a good case study of how poorly the government sometimes keeps pace with the free market and consumer tastes, and how entrenched interests, even in the face of some creative map-drawing, can keep such a program aloft in the face of efforts to ground it.
. . .
The emptier the subsidized flights, it seems, the more cherished the program became. Members of Congress regularly pressured the Transportation Department to continue subsidies to towns they represented. A lobbying group sprang up solely to fight to preserve and expand the program.
For the full story, see:
 Source of the graphic: online version of the NYT article cited above.
Source of the graphic: online version of the NYT article cited above.



 Nicholas D. Kristof. Source of image: online verison of the NYT commentary cited below.
Nicholas D. Kristof. Source of image: online verison of the NYT commentary cited below.

 Ful is a fava bean stew that is popular in Cairo. Source of image: online version of the NYT article cited above.
Ful is a fava bean stew that is popular in Cairo. Source of image: online version of the NYT article cited above.

 Hernando de Soto and Bill Clinton at the second annual Clinton Global Initiative. Source of photo: online version of the WSJ article cited below.
Hernando de Soto and Bill Clinton at the second annual Clinton Global Initiative. Source of photo: online version of the WSJ article cited below.