“The economy ‘will remain challenging for a long time,’ says IKEA Chief Executive Mikael Ohlsson.” Source of caption and photo: online version of the WSJ article quoted and cited below.
“The economy ‘will remain challenging for a long time,’ says IKEA Chief Executive Mikael Ohlsson.” Source of caption and photo: online version of the WSJ article quoted and cited below.
(p. B3) MALMO, Sweden–IKEA is poised to embark on a global spending spree, but its departing chief executive says red tape is slowing how fast the home-furnishings retailer can open its pocket book.
With the company set to report record sales on Wednesday, CEO Mikael Ohlsson said the amount of time it takes to open a store has roughly doubled in recent years.
“What some years ago took two to three years, now takes four to six years. And we also see that there’s a lot of hidden obstacles in different markets and also within the [European Union] that’s holding us back,” he said in an interview recently at an IKEA store on Sweden’s western coast.
. . .
IKEA plans to invest €2 billion in stores, factories and renewable energy this year. But the company fell €1 billion short of its goal of investing €3 billion in new projects last year, largely because of bureaucratic obstacles, he said. For 10 years IKEA has tried unsuccessfully to relocate a store in France, for example. The company also is challenging German policy dictating what can be sold and where, saying the rules are out of sync with EU legislation.
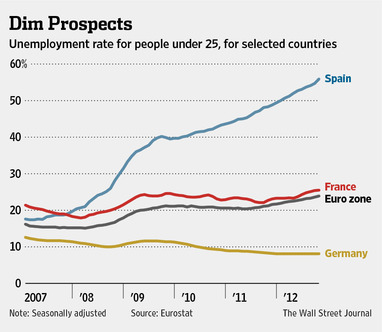
“It’s a pity, because it can help create jobs and investments at a time when unemployment is high in many countries,” Mr. Ohlsson said. A new IKEA store creates construction and store jobs for about 1,000 workers, he said.
. . .
The company’s highest-profile headaches have come in India, an untapped market where IKEA wants to open a first store in at least five years and roll out an additional three soon thereafter.
For the full story, see:
ANNA MOLIN. “IKEA Chief Takes Aim at Red Tape.” The Wall Street Journal (Weds., January 23, 2013): B3.
(Note: ellipses added.)
(Note: the online version of the story has the date January 22, 2013.)