Source of the images: screen captures from the CNN report cited below.
With self-righteous indignation, the left often accuses the right of “McCarthyism.”
But many on the left are happy to limit free speech when what is spoken is not to their liking.
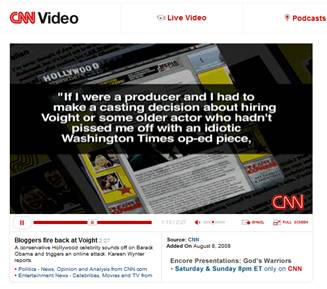
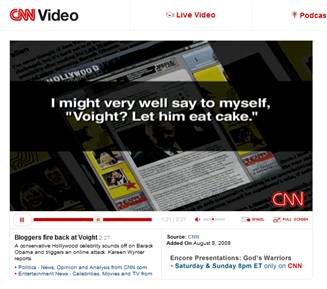
Jon Voight’s column in the Washington Times has ignited a firestorm, and caused at least one Hollywood insider to openly advocate blacklisting Voight from the movie business. The CNN story cited and linked below, gives some of the details.
Unfortunately, this is not an isolated example.
On our campuses, free speech is often violated if the speaker speaks what is not politically correct. For many examples, see some of the cases discussed on the web site of the Foundation for Individual Rights in Education.
Another example is from my own personal experience as a young scholar many decades ago. I had applied to three or four top PhD programs in philosophy and was initially rejected from every one of them, even though I had a nearly perfect GPA, and very high test scores.
I was especially surprised by the rejection from Chicago, because an Associate Dean had visited the Wabash campus the year before and talked with me about applying to Chicago. He had looked at my record and said, ‘with your record, if you score X, or above on the GREs, it is almost certain that you will be accepted.’ (I don’t remember the exact number he said.) Well I scored above X, but was rejected. So I wrote to the Associate Dean, saying I was disappointed and asking if he had any insight about the rejection. He told me that he was dumbfounded and that he would look into it.
Awhile later, I received a letter reversing the decision of the University of Chicago Department of Philosophy. I never learned all the details, but apparently the Dean of Humanities had over-ruled the Department of Philosophy. (This is fairly unusual in academics, and though I do not remember her name, I salute that Dean for taking a stand.)
Years later, the episode came up in a conversation with a member of the philosophy faculty. He said that he had been on the admissions committee the year that I had applied, and that I had been rejected because I had mentioned Ayn Rand in my essay about how I had become interested in philosophy.
For some of the details of the Voight story, see:
Wynter, Kareen. “Bloggers Fire Back at Voight.” CNN Feature, broadcast on CNN, and posted on CNN.com on 8/8/08. Downloaded on 8/8/08 from: http://www.cnn.com/video/?iref=videoglobal
(Note: the clip runs 2 minutes and 27 seconds.)
Voight’s op-ed piece ran in the Washington Times on July 28, 2008 under the title “My Concerns for America” and can be viewed at: http://www.washingtontimes.com/news/2008/jul/28/voight/









