Source of graph: online version of the NYT article quoted and cited below.
(p. A1) “Tonight, I propose a new tax cut for homeownership that says to every middle-income working family in this country, if you sell your home, you will not have to pay a capital gains tax on it ever — not ever.”
— President Bill Clinton, at the 1996 Democratic National Convention
Ryan J. Wampler had never made much money selling his own homes.
Starting in 1999, however, he began to do very well. Three times in eight years, Mr. Wampler — himself a home builder and developer — sold his home in the Phoenix area, always for a nice profit. With prices in Phoenix soaring, he made almost $700,000 on the three sales.
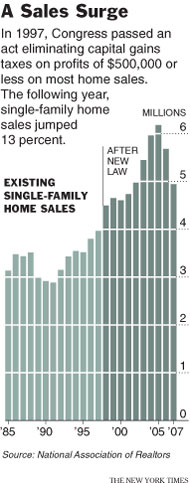
And thanks to a tax break proposed by President Bill Clinton and approved by Congress in 1997, he did not have to pay tax on most of that profit. It was a break that had not been available to generations of Americans before him. The benefits also did not apply to other investments, be they stocks, bonds or stakes in a small business. Those gains were all taxed at rates of up to 20 percent.
The different tax treatments gave people a new incentive to plow ever more money into real estate, and they did so. “When you give that big an incentive for people to buy and sell homes,” said Mr. Wampler, 44, a mild-mannered native of Phoenix who has two children, “they are going to buy and sell homes.”
By itself, the change in the tax law did not cause the housing bubble, economists say. Several other factors — a relaxation of lending standards, a failure by regulators to intervene, a sharp decline in interest rates and a collective belief that house prices could never fall — probably played larger roles.
But many economists say that (p. A22) the law had a noticeable impact, allowing home sales to become tax-free windfalls. A recent study of the provision by an economist at the Federal Reserve suggests that the number of homes sold was almost 17 percent higher over the last decade than it would have been without the law.
Vernon L. Smith, a Nobel laureate and economics professor at George Mason University, has said the tax law change was responsible for “fueling the mother of all housing bubbles.”
For the full story, see:
VIKAS BAJAJ and DAVID LEONHARDT. “1997 Tax Break on Home Sales May Have Helped Inflate Bubble.” The New York Times (Fri., December 19, 2008): A1 & A22.
(Note: ellipses added.)
(Note: the online version of the article is dated December 18, and has the somewhat different title: “The Reckoning; Tax Break May Have Helped Cause Housing Bubble.”)
 “Ryan J. Wampler made nearly $700,000 on three sales of his own homes in eight years.” Source of caption and photo: online version of the NYT article quoted and cited above.
“Ryan J. Wampler made nearly $700,000 on three sales of his own homes in eight years.” Source of caption and photo: online version of the NYT article quoted and cited above.




