 Source of graphic: online version of the WSJ article cited below.
Source of graphic: online version of the WSJ article cited below.
(p. A1) The so-called Doha round of talks, which began in 2001, were designed to boost developing nations; among other things, they want lower barriers to their agricultural exports. France has vowed to veto any deal that doesn’t protect its farmers. A pivotal missed deadline April 30 has led to predictions the talks could die by summer if countries including France don’t change their stance.
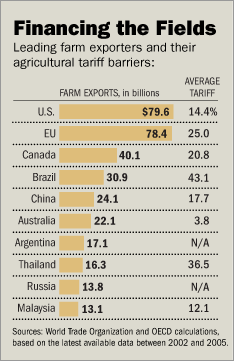
The standoff shows how cultural and emotional factors can combine with politics to stifle free-trade goals that most economists believe would provide a net benefit to the world. The tariff cuts envisioned by Doha would not only help developing countries sell their minerals and food products, but would also lower barriers to the industrialized world’s exports of goods and services. The World Bank calculates that Doha would boost the global economy by around $100 billion.
Overall, France itself likely would be a major economic gainer from a global (p. A10) deal. Though it’s the world’s second-largest agriculture exporter after the U.S., farming accounts for just 2.5% of the French economy. World-class manufacturing and service companies, such as car maker Renault SA and insurer AXA SA, are larger engines of the French economy. France could gain more income than it would lose in opening its agricultural markets to budding farm superpowers like Brazil.
Even in agriculture, France can be a formidable competitor, notably in products such as wine and cheese. Its brand is well-known the world over. And its farms are increasingly home to capital-intensive agribusiness companies, not just small family producers. Most of the $11.5 billion in European Union subsidies that France receives each year goes to the largest, most commercially viable farms.
WTO chief Pascal Lamy, a Frenchman, says he doesn’t understand France’s position. "As an efficient farm producer, the strategy should be to reduce subsidies and prices, because others won’t be able to compete with you," he said in a recent interview.
. . .
The French rural tradition, however, is changing. Between 1993 and 2004, the number of arable farms fell by nearly a third. Wide swaths of neglected land are now home to unsightly scrub, and the farms people see as they drive down France’s immaculate highways are often parts of major business enterprises. Oxfam says as much as 60% of subsidies went to the richest 15% of French farmers in 2004, the latest figures available.
Oxfam believes the EU’s tariffs and farm subsidies, which total over €40 billion annually, are harmful to the world’s poorest countries. High customs duties keep products from poor nations out of the wealthy EU market. At the same time, EU farmers overproduction is dumped cheaply abroad, driving down global prices and harming farmers in the developing world.
For the full story, see:
SCOTT MILLER. "Food Fight; French Resistance To Trade Accord Has Cultural Roots; WTO Talks Promise Benefits But Farmers Retain Hold On the Nation’s Stomach; ‘Politicians Are Frightened’." The Wall Street Journal (Tues., May 16, 2006): A1 & A10.
