 A view of part of the Greenland ice sheet. Source of the photo: online version of the NYT article quoted and cited below.
A view of part of the Greenland ice sheet. Source of the photo: online version of the NYT article quoted and cited below.
(p. D3) OSLO — Mainstream climatologists who have feared that global warming could have the paradoxical effect of cooling northwestern Europe or even plunging it into a small ice age have stopped worrying about that particular disaster, although it retains a vivid hold on the public imagination.
The idea, which held climate theorists in its icy grip for years, was that the North Atlantic Current, an extension of the Gulf Stream that cuts northeast across the Atlantic Ocean to bathe the high latitudes of Europe with warmish equatorial water, could shut down in a greenhouse world.
Without that warm-water current, Americans on the Eastern Seaboard would most likely feel a chill, but the suffering would be greater in Europe, where major cities lie far to the north. Britain, northern France, the Low Countries, Denmark and Norway could in theory take on Arctic aspects that only a Greenlander could love, even as the rest of the world sweltered.
All that has now been removed from the forecast. Not only is northern Europe warming, but every major climate model produced by scientists worldwide in recent years has also shown that the warming will almost certainly continue.
“The concern had previously been that we were close to a threshold where the Atlantic circulation system would stop,” said Susan Solomon, a senior scientist at the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. “We now believe we are much farther from that threshold, thanks to improved modeling and ocean measurements. The Gulf Stream and the North Atlantic Current are more stable than previously thought.”
. . .
“The ocean circulation is a robust feature, and you really need to hit it hard to make it stop,” said Eystein Jansen, a paleoclimatologist who directs the Bjerknes Center for Climate Research, also in Bergen. “The Greenland ice sheet would not only have to melt, but to dynamically disintegrate on a huge scale across the entire sheet.”
The worst imaginable collapse would likely take centuries to play out, he said. Any disruption to the North Atlantic Current — whose volume is 30 times greater than all the rivers in the world combined — would thus occur beyond the time horizon of the United Nations climate panel.
For the full story, see:
(Note: ellipsis added.)
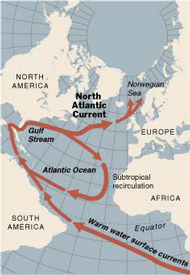 Source of the map: online version of the NYT article quoted and cited above.
Source of the map: online version of the NYT article quoted and cited above.
