 “Ahmed Muhammad Sayyid, center, praying at a Cairo mosque, has drawn religion closer after many disappointments.” Source of caption and photo: online version of the NYT article quoted and cited below.
“Ahmed Muhammad Sayyid, center, praying at a Cairo mosque, has drawn religion closer after many disappointments.” Source of caption and photo: online version of the NYT article quoted and cited below.
(p. 1) Here in Egypt and across the Middle East, many young people are being forced to put off marriage, the gateway to independence, sexual activity and societal respect. Stymied by the government’s failure to provide adequate schooling and thwarted by an economy without jobs to match their abilities or aspirations, they are stuck in limbo between youth and adulthood.
“I can’t get a job, I have no money, I can’t get married, what can I say?” Mr. Sayyid said one day after becoming so overwhelmed that he refused to go to work, or to go home, and spent the day hiding at a friend’s apartment.
In their frustration, the young are turning to religion for solace and purpose, pulling their parents and their governments along with them.
. . .
The wave of religious identification has forced governments that are increasingly seen as corrupt or inept to seek their own public redemption through religion.
. . .
(p. 11) Depression and despair tormented dozens of men and women in their 20s interviewed across Egypt, from urban men like Mr. Sayyid to frustrated village residents like Walid Faragallah, who once hoped education would guarantee him social mobility. Their stifled dreams stoke anger toward the government.
“Nobody cares about the people,” Mr. Sayyid said, slapping his hands against the air, echoing sentiment repeated in many interviews with young people across Egypt. “Nobody cares. What is holding me back is the system. Find a general with children and he will have an apartment for each of them. My government is only close to those close to the government.”
. . .
Mr. Sayyid’s path to stalemate began years ago, in school.
Like most Egyptians educated in public schools, his course of study was determined entirely by grades on standardized tests. He was not a serious student, often skipping school, but scored well enough to go on to an academy, something between high school and a university. He was put in a five-year program to study tourism and hotel operations.
His diploma qualified him for little but unemployment. Education experts say that while Egypt has lifted many citizens out of il-(p. 12)literacy, its education system does not prepare young people for work in the modern world. Nor, according to a recent Population Council report issued in Cairo, does its economy provide enough well-paying jobs to allow many young people to afford marriage.
Egypt’s education system was originally devised to produce government workers under a compact with society forged in the heady early days of President Gamal Abdel Nasser’s administration in the late 1950s and ’60s.
Every graduate was guaranteed a government job, and peasant families for the first time were offered the prospect of social mobility through education. Now children of illiterate peasant farmers have degrees in engineering, law or business. The dream of mobility survives, but there are not enough government jobs for the floods of graduates. And many are not qualified for the private sector jobs that do exist, government and business officials said, because of their poor schooling. Business students often never touch a computer, for example.
On average, it takes several years for graduates to find their first job, in part because they would rather remain unemployed than work in a blue-collar factory position. It is considered a blow to family honor for a college graduate to take a blue-collar job, leaving large numbers of young people with nothing to do.
“O.K., he’s a college graduate,” said Muhammad el-Seweedy, who runs a government council that has tried with television commercials to persuade college graduates to take factory jobs and has provided training to help improve their skills. “It’s done. Now forget it. This is a reality.”
But more widespread access to education has raised expectations. “Life was much more bearable for the poor when they did accept their social status,” said Galal Amin, an economist and the author of “Whatever Happened to the Egyptians?” “But it is unimaginable when you have an education, to have this thought accepted. Frustration opens the door to religiosity.”
For the full story, see:
MICHAEL SLACKMAN. “Generation Faithful; Dreams Stifled, Egypt’s Young Turn to Islamic Fervor.” The New York Times, First Section (Sun., February 17, 2008): 1 & 11-12.
(Note: ellipses added.)
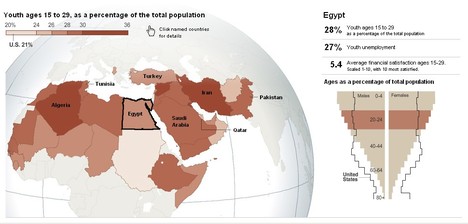 Source of graphic: online version of the NYT article quoted and cited above.
Source of graphic: online version of the NYT article quoted and cited above.
