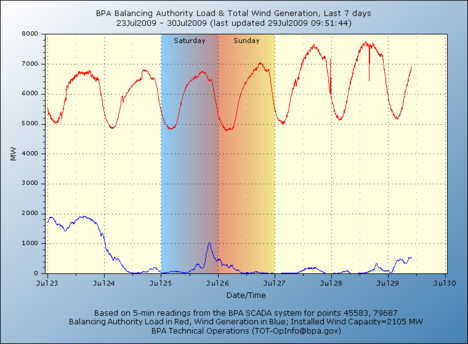
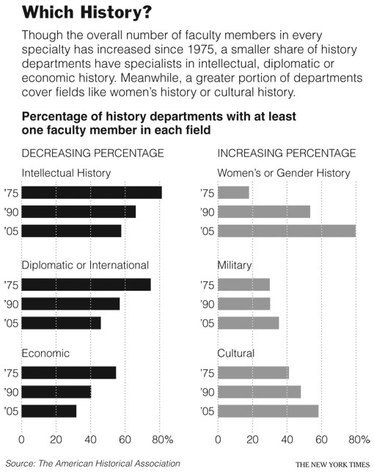
In the commentary quoted below, “LTCM” stands for the Long-Term Capital Management hedge fund.
(p. A25) Because families without the real economic means to repay traditional 30-year mortgages were getting them, housing prices grew to artificially high levels.
This is where the real sin of Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac comes into play. Both were created by Congress to make housing affordable to the middle class. But when they began guaranteeing subprime loans, they actually began pricing out the working class from the market until the banking business responded with ways to make repayment of mortgages allegedly easier through adjustable rates loans that start off with low payments. But these loans, fully sanctioned by the government, were a ticking time bomb, as we’re all now so painfully aware.
A similar bomb exploded in 1998, when LTCM blew up. The policy response to the LTCM debacle is instructive; more than anything else it solidified Wall Street’s belief that there were little if any real risks to risk-taking. With $5 billion under management, LTCM was deemed too big to fail because, with nearly every major firm copying its money losing trades, much of Wall Street might have failed with it.
That’s what the policy makers told us anyway. On Wall Street there’s general agreement that the implosion of LTCM would have tanked one of the biggest risk takers in the market, Lehman Brothers, a full decade before its historic bankruptcy filing. Officials at Merrill, including its then-CFO (and future CEO) Stan O’Neal, believed Merrill’s risk-taking in esoteric bonds could have led to a similar implosion 10 years before its calamitous merger with Bank of America.
We’ll never know if LTCM’s demise would have tanked the financial system or simply tanked a couple of firms that bet wrong. But one thing is certain: A valuable lesson in risk-taking was lost. By 2007, the years of excessive risk-taking, aided and abetted by the belief that the government was ready to paper over mistakes, had taken their toll.
With so much easy money, with the government always ready to ease their pain, Wall Street developed new and even more innovative ways to make money through risk-taking.
For the full commentary, see:
CHARLES GASPARINO. “Three Decades of Subsidized Risk; There’s a reason Dick Fuld didn’t believe Lehman would be allowed to fail.” The Wall Street Journal (Fri., NOVEMBER 6, 2009): A25.