 "A vendor sold bread on Wednesday in a poor section of Cairo, where lines are long and customers pushy." Source of caption and photo: online version of the NYT article quoted and cited below.
"A vendor sold bread on Wednesday in a poor section of Cairo, where lines are long and customers pushy." Source of caption and photo: online version of the NYT article quoted and cited below.
(p. A4) Much of what ails Egypt seems to converge in the story of subsidized bread. It speaks to a state that is in many ways stuck in the past, struggling to pull itself into the future, unable, or unwilling, to conquer corruption or even to persuade people to care about one another.
How do you take a broken system that somehow helps feed 80 million people and fix it without causing social disorder? That is a challenge for Egypt at large, and for this little bakery where Mr. Muhammad ekes out a living, with a cigarette hanging from his lips and an angry crowd demanding his bread.
. . .
“The most corrupt sector in the country is the provisions sector,” said a government inspector who asked not to be identified for fear of punishment. His job is to go to bakeries to ensure they are actually using the cheap government flour to produce cheap bread that is sold at the proper price.
The inspector explained why the system was so open to abuse. The government sells bakeries 25-pound bags of flour for 8 Egyptian pounds, the equivalent of about $1.50. The bakeries are then supposed to sell the flatbread at the subsidized rate, which gives them a profit of about $10 from each sack. Or the baker can simply sell the flour on the black market for $15 a bag.
If the inspector, who said he was paid $42 a month, certifies that after three months the baker has faithfully used the flour to bake bread, the baker gets a refund of about $1 a bag. A baker who goes through 40 sacks a day over the three-month period gets back 18,000 pounds (around $3,300) — a nice sum, this inspector said, which could easily be shared with an underpaid inspector.
. . .
Over the course of an hour one recent day, 14-year-old Mahmoud Ahmed managed four trips to the counter. His job, he said, was to ensure a steady stream of bread for a nearby food vendor, who then resold it in sandwiches. It appeared that the baker let him push his way to the front to get bread before others. Was there a deal going? Mahmoud would not say.
Down the road, five blocks away, a 12-year-old, Muhammad Abdul Nabi, was selling bread, the same kind of bread, from a makeshift table for more than double the price at the bakery. But there were no lines.
For the full story, see:
(Note: ellipses added.)
 "Fresh baked for less than a penny, and that’s just the start of the complications." Source of caption and photo: online version of the NYT article quoted and cited above.
"Fresh baked for less than a penny, and that’s just the start of the complications." Source of caption and photo: online version of the NYT article quoted and cited above.

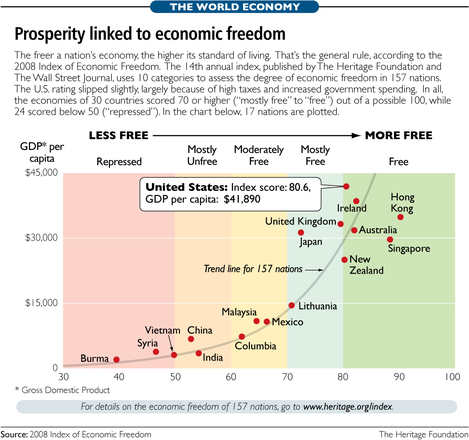
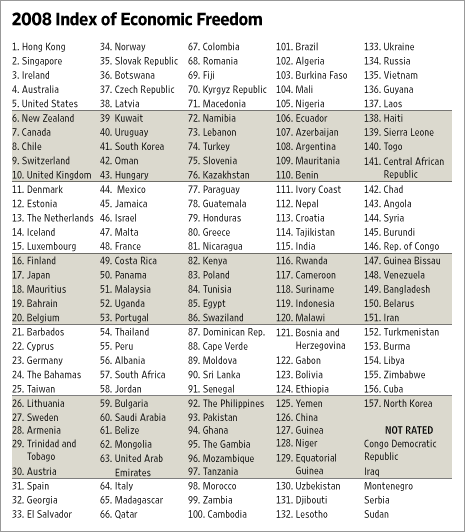 Source of table: online version of the WSJ article quoted and cited above.
Source of table: online version of the WSJ article quoted and cited above.

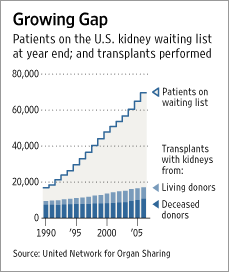 Source of graphic: online version of the WSJ article quoted and cited below.
Source of graphic: online version of the WSJ article quoted and cited below. Source of image: online version of the WSJ article quoted and cited above.
Source of image: online version of the WSJ article quoted and cited above. "Thor Halvorssen at his office in the Empire State Building." Source of caption and photo: online version of the NYT article quoted and cited below.
"Thor Halvorssen at his office in the Empire State Building." Source of caption and photo: online version of the NYT article quoted and cited below.

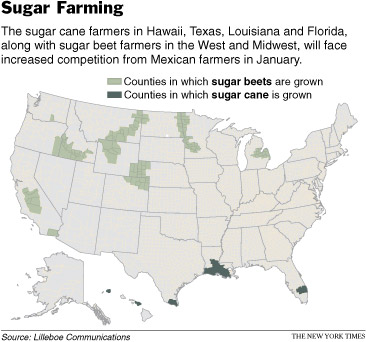 Source of graphic: online version of NYT article cited above.
Source of graphic: online version of NYT article cited above.
 Sally Satel is a medical doctor and a resident scholar at the Amerrican Enterprise Institute. Source of photo:
Sally Satel is a medical doctor and a resident scholar at the Amerrican Enterprise Institute. Source of photo: 
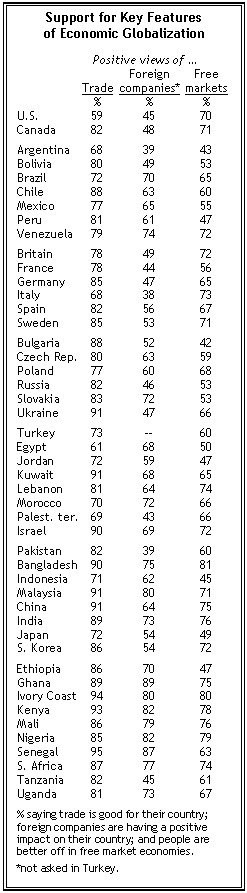 Source of table: "World Publics Welcome Global Trade — But Not Immigration." Pew Global Attitudes Project, a project of the PewResearchCenter. Released: 10.04.07 dowloaded from:
Source of table: "World Publics Welcome Global Trade — But Not Immigration." Pew Global Attitudes Project, a project of the PewResearchCenter. Released: 10.04.07 dowloaded from: