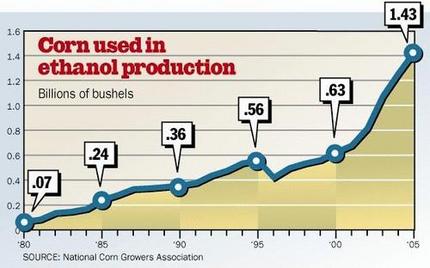
 Source of graphics: online version of the World-Herald article cited below.
Source of graphics: online version of the World-Herald article cited below.
(p. 1D) LINCOLN – David Pimentel, a Cornell University researcher, has been criticized repeatedly since he questioned the energy value of ethanol in 1980.
In a government-funded report, he suggested that ethanol provides less energy than is used to produce it. Even though that report has been disputed and rejected by other analysts, Pimentel has not backed down.
He said last week that rural developers, farmers and investors will rue the day they put their money, hopes and dreams into the corn-based alternative fuel.
"It is too bad," he said in an interview, "because it would be a tremendous asset to agriculture if this were a true winner."
Pimentel is among the public critics who raise red flags as momentum gathers for dramatic increases in production, especially in the nation’s top two ethanol-producing states: Iowa and Nebraska.
While Pimentel is perhaps the expert most often quoted – in part because he presented his analysis more than 25 years ago – others also raise questions about the energy value of ethanol and its economic benefits and environmental effects.
Ethanol backers defend the fuel as a viable way to help stabilize the nation’s fuel supply. But they haven’t convinced Jerry Taylor, an energy policy specialist for the Cato Institute, a conservative think tank in Washington, D.C.
"If ethanol made economic sense, it wouldn’t need a subsidy," Taylor said.
For the full story, see:
BILL HORD. "High-octane Clash." Omaha World-Herald (Sunday, August 6, 2006): 1D-2D.
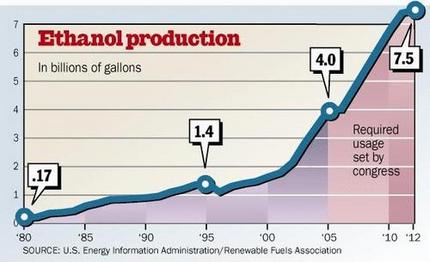
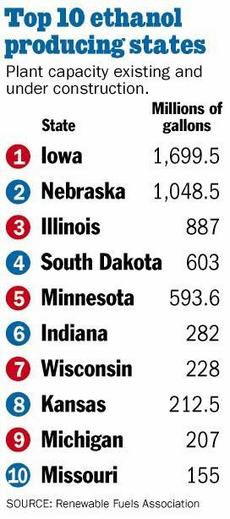 Source of graphics: online version of the World-Herald article cited above.
Source of graphics: online version of the World-Herald article cited above.

 Canon’s new HV10 high definition camcorder. Source of image: the NYT article cited below.
Canon’s new HV10 high definition camcorder. Source of image: the NYT article cited below.

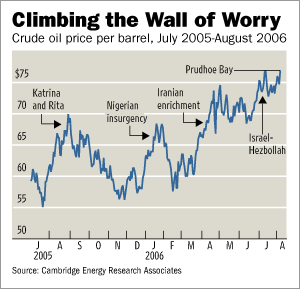 Source of graphic: online version of the WSJ article cited below.
Source of graphic: online version of the WSJ article cited below.