 Sally Satel is a medical doctor and a resident scholar at the Amerrican Enterprise Institute. Source of photo: http://www.aei.org/publications/filter.all,pubID.25785/pub_detail.asp
Sally Satel is a medical doctor and a resident scholar at the Amerrican Enterprise Institute. Source of photo: http://www.aei.org/publications/filter.all,pubID.25785/pub_detail.asp
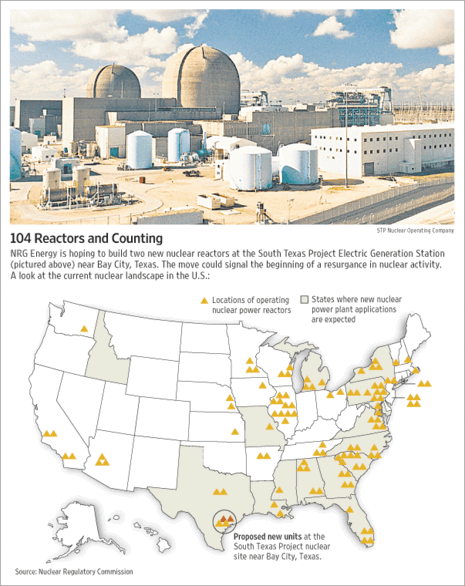
(p. A12) At the annual meeting of The American Society of Transplant Surgeons this winter a straw poll revealed that 80 to 85% were in favor of studying incentives for living donors, according to society president Arthur Matas. In 2003, the American Medical Association testified on behalf of legislation that would have permitted pilot studies of incentives for deceased organs.
The public seems receptive as well, according to a new Gallup poll on attitudes toward donation of organs after death. The most striking results were among 18 to 34 year olds wherein an impressive 34% said that incentives would make them "more likely" to donate while 6% said less likely. . . .
. . .
The idea of combining organ donation with material gain can make people queasy. Yet the mix of financial and humanitarian motives is commonplace. No one objects, for example, to a tax credit for charitable contributions–a financial incentive to complement the "pure" motive of giving to others. The great teachers who enlighten us and the doctors who heal us inspire no less gratitude because they are paid. An increase in the supply of kidneys will ameliorate suffering and prevent needless death. This is more important than whether an organ has been given freely or for material gain. . . .
For the full commentary, see:
Satel, Sally. "Doing Well By Doing Good." The Wall Street Journal (Fri, March 16 2007): A12.
(Note: ellipses added.)


 (Note: ellipses added.)
(Note: ellipses added.)
 Columnist Bob Herbert. Source of photo: online version of the NYT column quoted and cited above.
Columnist Bob Herbert. Source of photo: online version of the NYT column quoted and cited above.

 (Note: ellipsis in Rearden quote was in original; the other two ellipses were added.)
(Note: ellipsis in Rearden quote was in original; the other two ellipses were added.)